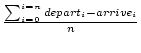Next: Parallel Discrete Event Simulation
Up: General Principles
Previous: World Views
Example 3.1: Able and Baker, revisited.
- System state:
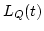 : the number of cars waiting to be served at
time t.
: the number of cars waiting to be served at
time t.
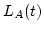 : a boolean variable indicating Able being
idle or busy at the time.
: a boolean variable indicating Able being
idle or busy at the time.
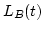 : a boolean variable indicating Baker being
idle or busy at the time.
: a boolean variable indicating Baker being
idle or busy at the time.
- Entities: cars and the two servers.
- Events:
- arrival event
- service complete by Able event.
- service complete by Baker event.
- Activities:
- interarrival time
- Able's service time
- Baker's service time
- Delay: a customer's wait in the queue until Able or Baker is free.
Example 3.3: Single-channel queue (Supermarket check-out counter).
In conducting an event-scheduling simulation, a simulation table is
used to record the successive system snap-shots as time advances.
The simulation table is Table 3.1 on page 72.
- System state:
- (LQ(t), LS(t)) where LQ(t) is the number of
customers in waiting line, and LS(t) is the number of customers in
service at time t.
- Entities:
- Server and customers.
- Events:
-
- Arrival (A)
- Departure (D)
- Stopping event (E), scheduled to occur at time 60.
- Event notices:
-
- (A,t) representing an arrival event to occur at future
time t.
- (D,t) representing a departure event to occur at future
time t.
- (E,60) representing the stopping event to occur at future
time 60.
- Activities:
-
- Interarrival time, defined in Table 2.6 page 28.
- Service time, defined in Table 2.7 page 28.
Example 3.4: The check-out counter simulation, continued.
Further from Example 3.3, we want to collect some statistics, mean
response time and mean proportion of customers who spend 4 or more
minutes in the system (time in the system includes waiting time
and service time).
- mean response time =
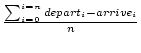
- mean proportion of the customers who spend 4 or or minutes
=
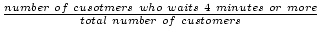
Example 3.5: The dump truck problem.
- Six dump trucks haul coal from the entrance of small mine to
the railroad.
- Each truck is loaded by one of the two loaders.
- After loading, a truck moves immediately to the scale to be
weighed as soon as the scale is available.
- The two loaders and the scal have a first-come-first-server queue.
- The actual time for loading and weighing is negligible.
- Aftger being weighed, the truck drives off and will come
back to the same line, to get smore coal. This process is repeated.
The model has following components.
- System state: [LQ(t), L(t), WQ(t), W(t)]
- LQ(t) = number of trucks in loader queue
- L(t) = number of trucks in loader (0, 1, 2)
- WQ(t) = number of trucks in scale's waiting
queue.
- W(t) = number of trucks being weighed (0, 1, or
).
- Event notices
- (ALQ, t, DTi) dump truck i arrives at loader queue
- (EL, t, DTi) dump truck i end ends loading at
 being loaded.
being loaded.
- (EW, t, DTi) dump truck i ends weighing at time t.
- Entities: The six dump trucks (DT1, DT2, ..., DT6)
- Lists: loader queue and scale queue, both first-in-first-out.
- Activites: Loading time, weighing time, and travel time.
- Delay: Delay at loader queue, and the scale.
See Table 3.6 on page 77 for an illustration.



Next: Parallel Discrete Event Simulation
Up: General Principles
Previous: World Views
Meng Xiannong
2002-10-18
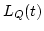 : the number of cars waiting to be served at
time t.
: the number of cars waiting to be served at
time t.
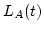 : a boolean variable indicating Able being
idle or busy at the time.
: a boolean variable indicating Able being
idle or busy at the time.
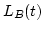 : a boolean variable indicating Baker being
idle or busy at the time.
: a boolean variable indicating Baker being
idle or busy at the time.