- How much current flows through the lamp bulb when it is on?
- What is the equivalent resistance of the lamp bulb when it is on?
1.30 (combine series/parallel resistors and use voltage dividers)
1.45 (dependent source)
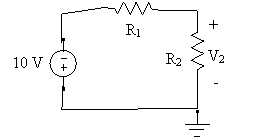
- If R1 has value 500 ohms, what is the value of the voltage Vsensor at room temperature and at body temperature? What is the difference in Vsensor at the two temperatures?
- What value for R1 maximizes the difference in Vsensor at the two temperatures?
